Table of Contents
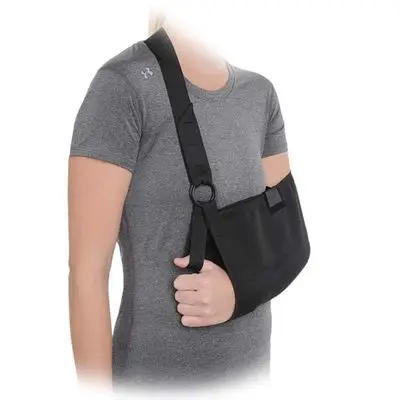
Arm Sling
An arm sling is a supportive medical device designed to immobilize and support the arm, typically after an injury, surgery, or when recovering from a condition that affects the arm, shoulder, or wrist. Slings are commonly used to help reduce pain, prevent further injury, and facilitate healing by keeping the arm in a neutral and stable position.
Uses of an Arm Sling
- Post-Surgery Recovery: After surgeries such as shoulder repairs, rotator cuff surgery, or elbow procedures, an arm sling helps immobilize the area and prevent unnecessary movement.
- Fractures: Used for fractures of the arm, collarbone (clavicle), or shoulder blade (scapula) to keep the arm stable while healing.
- Dislocations: A sling can help immobilize the arm after a shoulder or elbow dislocation, preventing further injury and allowing the joint to heal.
- Strains and Sprains: Slings provide support for muscles or ligaments that have been strained or sprained, limiting movement to promote healing.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like arthritis or bursitis may require the use of a sling to reduce strain on the affected joints.
Types of Arm Slings
Standard Arm Sling
- Design: A simple fabric pouch that supports the forearm, secured with a strap that goes around the neck or shoulder.
- Uses: Common for mild injuries, fractures, or post-surgical recovery.
Shoulder Immobilizer Sling
- Design: Includes a strap that wraps around the waist to prevent the arm from moving away from the body.
- Uses: Often used after shoulder surgeries or dislocations to fully immobilize the shoulder joint.
Abduction Sling
- Design: A specialized sling with a pillow or wedge that keeps the arm slightly away from the body (abducted position).
- Uses: Typically prescribed after rotator cuff surgery or shoulder replacements to prevent internal rotation.
Elbow Immobilizer Sling
- Design: Focuses on stabilizing the elbow and limiting its movement, often with additional support at the elbow joint.
- Uses: Useful for elbow fractures or ligament injuries.
Benefits of an Arm Sling:
- Immobilization: Prevents movement of the injured arm, reducing pain and promoting healing.
- Pain Reduction: Keeping the arm in a stable position can help alleviate discomfort from injuries or surgical procedures.
- Support: Provides structural support for fractures, sprains, or muscle tears.
- Injury Prevention: Reduces the risk of further injury during the healing process by limiting movement.
Proper Usage Tips
- Positioning: The elbow should be at a 90-degree angle, and the hand should be slightly elevated above the elbow to reduce swelling.
- Comfort: The strap should not place excessive pressure on the neck; some slings come with padded straps to prevent neck strain.
- Doctor’s Instructions: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding the duration of use and specific care instructions for your injury.
Arm slings are an essential tool for anyone recovering from upper limb injuries or surgeries, providing the necessary support and immobilization to aid in healing.
Ergoactive Cane (Single)
SPECIFICATIONS
UNIT WEIGHT: 2.90 lbs
USER WEIGHT CAPACITY: 250 lbs
USER HEIGHT RANGE: 5'0" - 6'6"
CUFF SIZE: Standard
CUFF WIDTH: 3.50"
CUFF LENGHT: 7.00"
GRIP SIZE: Standard
GRIP DIAMETER: 1.75"
ERGOCAP (INCLUDED): High Performance (3/4")
GRIP ANGLE RANGE: 15º / 0º / -15º
GRIP (0º) TO CUFF (TOP) RANGE: 10.25" - 11.0"
FLOOR TO GRIP (0º) HEIGHT RANGE: 32.0" - 40.0"
OVERALL WIDTH: 4.50"
OVERALL DEPTH: 10.0"
FOLDED DIMENSIONS
HEIGHT: 26.5"
WIDTH: 4.50"
DEPTH: 10.0"
*MATERIALS ARE LATEX FREE
WARRANTY
Your ERGOBAUM forearm cane is warranted against defects in material and/or workmanship for one (1) year. This warranty does not extend to accessories and non-durable components, such as Ergo Cap crutch tips, grips, or soft goods which are subject to normal wear and replacement. Non-durable or consumable components are warranted against manufacturer defects for 30 days. The warranty does not extend to batteries, packaging, or packaging components (e.g. clips, ties, stickers).
If within such warranty period any such product shall be proven to be defective, such product shall be repaired or replaced at Ergoactives’ discretion. Refer to Ergoactives’ general Warranty Policy for further limitations and exclusions.
RETURN POLICY
This product is eligible for Ergoactives' standard 14-day money-back guarantee. Eligible returns must be returned in new, unused condition, packed in the original packaging and include all accessories, manuals and/or documentation that came with the product. Return shipping and any related costs are the responsibility of the customer. Returned merchandise is subject to a 40% restocking fee. To initiate a return, contact returns@ergoactives.com. Refer to Ergoactives’ Return Policy for further details and instructions.
INTERNATIONAL SHIPPING
CUSTOMS
You, the customer, are responsible for all taxes and duties (including VAT) imposed by your country of residence.
Ergoactives is not responsible for any packages held by international customs agencies and it is not the responsibility of Ergoactives to make the customer aware of these agencies and their actions. Please check with your country's customs office to determine their procedures and any potential charges.
Your package may arrive at your local post office or delivery center and be held until pickup and payment is taken care of.
If you neglect to pick up your package and it is returned to us, we will not refund the charge for original shipping.
Should Ergoactives mistakenly be invoiced directly for any duties or fees from the shipping company after delivery, we will email an invoice for the balance due. This will need to paid immediately.
As with domestic shipping, if a package can't be delivered due to an error entering your shipping address, Ergoactives is not responsible for any additional fees that may incur in order to reroute or reship the package.
TRACKING
If you have a USPS package marked as delivered but haven't received it, please contact your local mail facility.
You will have to pay taxes and duties in your own country if applicable. This is something we have no control over it and by purchasing an Ergoactives product, you acknowledge that you are aware of this and accept it as your financial responsibility.

Arm pain can result from a variety of causes, ranging from muscle strain to more serious conditions like nerve injuries or cardiovascular issues. The pain can be mild or severe, sharp or dull, and may be accompanied by other symptoms depending on the underlying cause.
Common Causes of Arm Pain
Muscle Strain or Overuse
- Cause: Overexertion from physical activities, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions (e.g., sports, typing, or manual labor).
- Symptoms: Aching, soreness, or stiffness in the muscles. Pain may worsen with movement.
- Treatment: Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE method), and over-the-counter pain relievers.
Injury or Trauma
- Cause: Fractures, sprains, or dislocations due to falls, accidents, or direct impact.
- Symptoms: Intense pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the arm.
- Treatment: Seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment. Fractures and dislocations may require casting, slings, or surgery.
Nerve Compression (e.g., Pinched Nerve)
- Cause: Nerve compression in the neck or shoulder area (cervical radiculopathy) or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Symptoms: Tingling, numbness, burning pain, or weakness in the arm, often radiating from the neck or shoulder.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or in severe cases, surgery.
Tendonitis or Bursitis
- Cause: Inflammation of tendons (tendonitis) or bursae (bursitis) due to overuse or repetitive motion.
- Symptoms: Localized pain around the joints, especially with movement or pressure.
- Treatment: Rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- Cause: Damage or tears in the shoulder’s rotator cuff, often from repetitive overhead movements or aging.
- Symptoms: Dull ache deep in the shoulder, pain when lifting the arm, and difficulty reaching behind the back.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgery in severe cases.
Heart-Related Causes (e.g., Heart Attack):
- Cause: Arm pain, particularly in the left arm, can be a symptom of a heart attack or angina.
- Symptoms: Pain radiating from the chest to the left arm, jaw, or back, along with shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea.
- Treatment: Seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
- Cause: Stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, often progressing over time.
- Symptoms: Pain and restricted movement in the shoulder, which can radiate to the arm.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgery in advanced cases.
Osteoarthritis:
- Cause: Wear and tear of cartilage in the joints, commonly affecting the shoulders or elbows.
- Symptoms: Pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint.
- Treatment: Pain management, physical therapy, and sometimes joint replacement surgery.
Referred Pain
- Cause: Pain in the arm caused by issues in other areas, such as the neck or spine.
- Symptoms: Pain that originates in the neck or spine but is felt in the arm.
- Treatment: Treat the underlying cause, such as cervical disc problems or nerve issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Sudden, severe pain: Especially if it’s accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness (potential heart attack).
- Pain after injury: If you suspect a fracture, dislocation, or severe sprain.
- Numbness or weakness: Persistent tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness may indicate nerve involvement.
- Swelling or deformity: Noticeable swelling, bruising, or visible deformities after trauma.
Treatment Options
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain.
- Ice/Heat Therapy: Ice packs for the first 48 hours to reduce swelling, followed by heat to relax muscles.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles and improve range of motion.
- Braces or Slings: Temporary support to immobilize the arm and promote healing.
- Surgery: For severe cases like fractures, dislocations, or tendon tears.
Prevention Tips
- Proper Ergonomics: Ensure good posture when working at a desk or using devices.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Regular exercises to strengthen arm and shoulder muscles.
- Avoid Repetitive Strain: Take breaks and use proper form during physical activities.
- Use Supportive Devices: Use braces or slings as recommended for injury prevention and recovery.
If arm pain persists or worsens, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.