Table of Contents
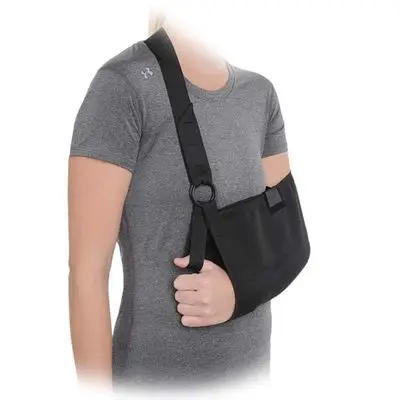
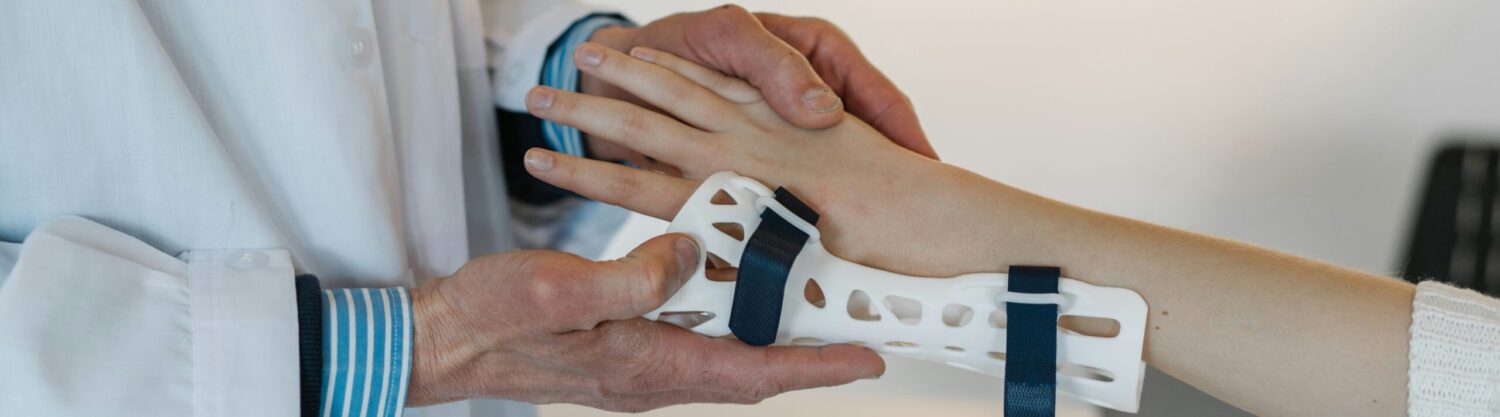
Arm Sling
An arm sling is a supportive medical device designed to immobilize and support the arm, typically after an injury, surgery, or when recovering from a condition that affects the arm, shoulder, or wrist. Slings are commonly used to help reduce pain, prevent further injury, and facilitate healing by keeping the arm in a neutral and stable position.
Uses of an Arm Sling
- Post-Surgery Recovery: After surgeries such as shoulder repairs, rotator cuff surgery, or elbow procedures, an arm sling helps immobilize the area and prevent unnecessary movement.
- Fractures: Used for fractures of the arm, collarbone (clavicle), or shoulder blade (scapula) to keep the arm stable while healing.
- Dislocations: A sling can help immobilize the arm after a shoulder or elbow dislocation, preventing further injury and allowing the joint to heal.
- Strains and Sprains: Slings provide support for muscles or ligaments that have been strained or sprained, limiting movement to promote healing.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like arthritis or bursitis may require the use of a sling to reduce strain on the affected joints.
Types of Arm Slings
Standard Arm Sling
- Design: A simple fabric pouch that supports the forearm, secured with a strap that goes around the neck or shoulder.
- Uses: Common for mild injuries, fractures, or post-surgical recovery.
Shoulder Immobilizer Sling
- Design: Includes a strap that wraps around the waist to prevent the arm from moving away from the body.
- Uses: Often used after shoulder surgeries or dislocations to fully immobilize the shoulder joint.
Abduction Sling
- Design: A specialized sling with a pillow or wedge that keeps the arm slightly away from the body (abducted position).
- Uses: Typically prescribed after rotator cuff surgery or shoulder replacements to prevent internal rotation.
Elbow Immobilizer Sling
- Design: Focuses on stabilizing the elbow and limiting its movement, often with additional support at the elbow joint.
- Uses: Useful for elbow fractures or ligament injuries.
Benefits of an Arm Sling:
- Immobilization: Prevents movement of the injured arm, reducing pain and promoting healing.
- Pain Reduction: Keeping the arm in a stable position can help alleviate discomfort from injuries or surgical procedures.
- Support: Provides structural support for fractures, sprains, or muscle tears.
- Injury Prevention: Reduces the risk of further injury during the healing process by limiting movement.
Proper Usage Tips
- Positioning: The elbow should be at a 90-degree angle, and the hand should be slightly elevated above the elbow to reduce swelling.
- Comfort: The strap should not place excessive pressure on the neck; some slings come with padded straps to prevent neck strain.
- Doctor’s Instructions: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding the duration of use and specific care instructions for your injury.
Arm slings are an essential tool for anyone recovering from upper limb injuries or surgeries, providing the necessary support and immobilization to aid in healing.
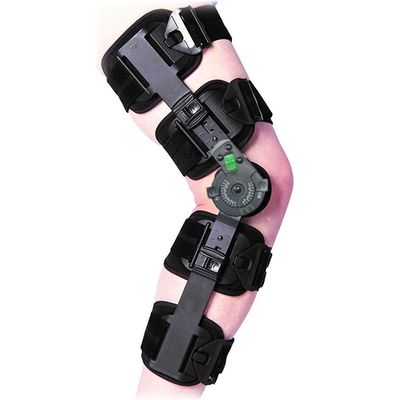
Ergoactive Knee Brace G1 KPA Post Op
The Ergoactives ErgoBrace is an adjustable, telescopic, over-motion post-op knee brace, designed to protect the knee joint and skin, using the most comfortable, lightweight materials while still providing superior support and adaptability
MADE OF LATEX-FREE ERGONOMIC MEDICAL GRADE MATERIALS
The ErgoBrace knee brace is made up of latex free medical grade materials. It has a special design aimed to protect the knee joint and the skin. It has a soft ergonomic plastic covering all of the metal parts of the brace close to the skin in order to avoid rashes or discomfort.
ONE-SIZE-FITS-ALL Universal Fit Adjustable
The ErgoBrace knee brace is a universal fit brace. It has multiple predetermined adjustment levels for adults of all sizes. The brace was designed to provide superior support and adjustability thanks to its unique height adjustable slider technology.
Hinged Immobilizer Technology for ACL, MCL, PCL Injuries
The ErgoBrace knee brace has a hinged immobilizer technology and range of motion limiter as well as over motion adjustability and lock up to 120 degrees. The user’s brace can be customized for all types of injuries and locked to any degree of motion. Just adjust the range of motion limiter to your desired position and it locks with the push of a button, staying in that position until unlocked by the user/medical practitioner by releasing the lock button.
Velcro straps, Long Lasting Breathable Comfort Pads, High Quality Plastic Buckles
The ErgoBrace knee brace contains multiple Velcro straps that allow the user to tighten the brace once positioned in the desired setting. The brace has breathable comfort pads that allow air to flow and do not retain sweat. It also has high quality plastic buckles to ensure that the velcro staps and the overall brace is in the correct position once placed in the user’s knee.
Washable and Reusable Materials
The ErgoBrace knee brace is made up of medical grade materials that are washable and reusable. In case of long term use, the user can wash the brace and make it look brand new as all materials are washable and reusable.
HIGHLIGHTS





SPECIFICATIONS
Height Range Above Hinge (Center): 9.50" - 12.5"
Height Range Below Hinge (Center): 9.50" - 12.5"
Circumference Range Above Hinge: 8.00" - 36.0"
Circumference Range Below Hinge: 8.00" - 22.0"
Range of Motion (ROM): 0º - 120º
Unit Weight: 2.20 lb
WARRANTY
RETURN POLICY
This product is non-returnable. It is considered a single-use patient item. Refer to Ergoactives’ Return Policy for further details.
INTERNATIONAL SHIPPING
CUSTOMS
You, the customer, are responsible for all taxes and duties (including VAT) imposed by your country of residence.
Ergoactives is not responsible for any packages held by international customs agencies and it is not the responsibility of Ergoactives to make the customer aware of these agencies and their actions. Please check with your country's customs office to determine their procedures and any potential charges.
Your package may arrive at your local post office or delivery center and be held until pickup and payment is taken care of.
If you neglect to pick up your package and it is returned to us, we will not refund the charge for original shipping.
Should Ergoactives mistakenly be invoiced directly for any duties or fees from the shipping company after delivery, we will email an invoice for the balance due. This will need to paid immediately.
As with domestic shipping, if a package can't be delivered due to an error entering your shipping address, Ergoactives is not responsible for any additional fees that may incur in order to reroute or reship the package.
TRACKING
If you have a USPS package marked as delivered but haven't received it, please contact your local mail facility.
You will have to pay taxes and duties in your own country if applicable. This is something we have no control over it and by purchasing an Ergoactives product, you acknowledge that you are aware of this and accept it as your financial responsibility.


Arm pain can result from a variety of causes, ranging from muscle strain to more serious conditions like nerve injuries or cardiovascular issues. The pain can be mild or severe, sharp or dull, and may be accompanied by other symptoms depending on the underlying cause.
Common Causes of Arm Pain
Muscle Strain or Overuse
- Cause: Overexertion from physical activities, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions (e.g., sports, typing, or manual labor).
- Symptoms: Aching, soreness, or stiffness in the muscles. Pain may worsen with movement.
- Treatment: Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE method), and over-the-counter pain relievers.
Injury or Trauma
- Cause: Fractures, sprains, or dislocations due to falls, accidents, or direct impact.
- Symptoms: Intense pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the arm.
- Treatment: Seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment. Fractures and dislocations may require casting, slings, or surgery.
Nerve Compression (e.g., Pinched Nerve)
- Cause: Nerve compression in the neck or shoulder area (cervical radiculopathy) or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Symptoms: Tingling, numbness, burning pain, or weakness in the arm, often radiating from the neck or shoulder.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or in severe cases, surgery.
Tendonitis or Bursitis
- Cause: Inflammation of tendons (tendonitis) or bursae (bursitis) due to overuse or repetitive motion.
- Symptoms: Localized pain around the joints, especially with movement or pressure.
- Treatment: Rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- Cause: Damage or tears in the shoulder’s rotator cuff, often from repetitive overhead movements or aging.
- Symptoms: Dull ache deep in the shoulder, pain when lifting the arm, and difficulty reaching behind the back.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgery in severe cases.
Heart-Related Causes (e.g., Heart Attack):
- Cause: Arm pain, particularly in the left arm, can be a symptom of a heart attack or angina.
- Symptoms: Pain radiating from the chest to the left arm, jaw, or back, along with shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea.
- Treatment: Seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
- Cause: Stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, often progressing over time.
- Symptoms: Pain and restricted movement in the shoulder, which can radiate to the arm.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgery in advanced cases.
Osteoarthritis:
- Cause: Wear and tear of cartilage in the joints, commonly affecting the shoulders or elbows.
- Symptoms: Pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint.
- Treatment: Pain management, physical therapy, and sometimes joint replacement surgery.
Referred Pain
- Cause: Pain in the arm caused by issues in other areas, such as the neck or spine.
- Symptoms: Pain that originates in the neck or spine but is felt in the arm.
- Treatment: Treat the underlying cause, such as cervical disc problems or nerve issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Sudden, severe pain: Especially if it’s accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness (potential heart attack).
- Pain after injury: If you suspect a fracture, dislocation, or severe sprain.
- Numbness or weakness: Persistent tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness may indicate nerve involvement.
- Swelling or deformity: Noticeable swelling, bruising, or visible deformities after trauma.
Treatment Options
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain.
- Ice/Heat Therapy: Ice packs for the first 48 hours to reduce swelling, followed by heat to relax muscles.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles and improve range of motion.
- Braces or Slings: Temporary support to immobilize the arm and promote healing.
- Surgery: For severe cases like fractures, dislocations, or tendon tears.
Prevention Tips
- Proper Ergonomics: Ensure good posture when working at a desk or using devices.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Regular exercises to strengthen arm and shoulder muscles.
- Avoid Repetitive Strain: Take breaks and use proper form during physical activities.
- Use Supportive Devices: Use braces or slings as recommended for injury prevention and recovery.
If arm pain persists or worsens, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.