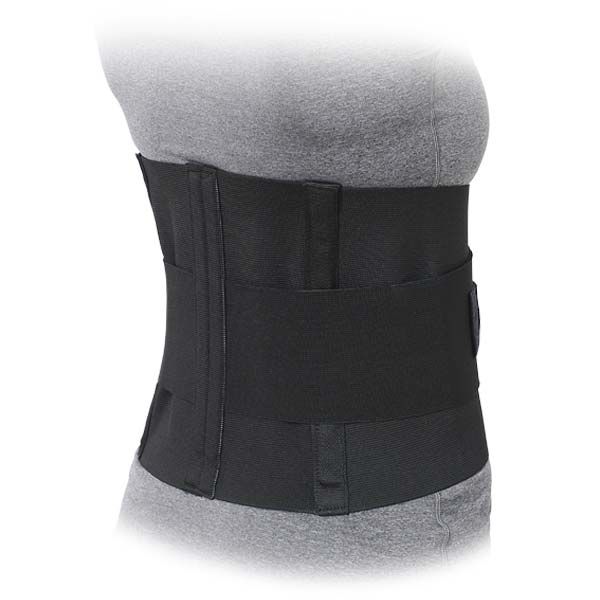
Lumbar Sacral = Back Support W/ Side Pulls
A back support with side pulls is a type of orthopedic brace designed to provide stability, compression, and support to the lower back, particularly in cases of lower back pain, injury, or strain. The addition of side pulls allows for adjustable compression and increased support, helping to alleviate pain and promote proper posture.
Key Features of a Back Support with Side Pulls
Adjustable Side Pulls
- Side pulls are adjustable straps or laces that allow users to tighten or loosen the brace as needed. This feature provides customizable compression and support to the lower back, enhancing comfort and effectiveness.
- The side pulls allow for easy adjustments throughout the day, accommodating changes in comfort level or activity.
Lumbar Support
- The brace is designed to target the lumbar region (lower back), providing support to the spine and surrounding muscles. This can help reduce stress on the back and prevent further injury.
Compression
- The compression provided by the brace helps reduce swelling and inflammation, which can lead to pain relief. Compression also promotes better posture and can improve muscle engagement in the lower back.
Breathable Material
- Many back supports with side pulls are made from breathable, moisture-wicking materials to ensure comfort during extended use. This helps reduce heat buildup and prevents skin irritation.
Ergonomic Design
- Designed to fit the natural curves of the back, the support is contoured to provide a snug and comfortable fit. The side pulls enable adjustments to fit a variety of body shapes and sizes.
Velcro or Hook-and-Loop Fastening
- The brace is usually secured with Velcro or hook-and-loop fasteners, allowing users to easily adjust the tightness for optimal support.
Uses of a Back Support with Side Pulls
Lower Back Pain Relief
- Ideal for people suffering from lower back pain due to muscle strain, overuse, or conditions like sciatica or herniated discs. The side pulls provide extra support to stabilize the lower back and alleviate pain.
Posture Improvement
- Helps correct poor posture by providing lumbar support and encouraging a more upright position. This can be particularly helpful for individuals who spend long hours sitting or standing in improper positions.
Injury Prevention
- Used by athletes, manual laborers, or individuals who perform heavy lifting to prevent lower back injuries. The brace adds extra stability to the spine and reduces the risk of strain or injury.
Post-Surgical Support
- Provides stability and reduces strain on the lower back following surgery or injury, promoting a faster recovery and preventing reinjury.
Chronic Back Conditions
- Beneficial for individuals with chronic back conditions such as degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, or lumbar stenosis. The adjustable side pulls allow for consistent support based on the level of discomfort.
Benefits of Back Support with Side Pulls
- Customizable Compression: The adjustable side pulls enable the user to tighten or loosen the brace, providing the right amount of compression based on activity level or pain.
- Improved Stability: By stabilizing the lower back and promoting proper posture, the brace helps reduce strain on the spine and surrounding muscles.
- Pain Relief: Compression and support can alleviate pain caused by injury, muscle strain, or chronic back conditions.
- Enhanced Mobility: Many users find that the brace allows them to continue daily activities with less pain, while still supporting their back.
How to Use a Back Support with Side Pulls
- Position the Brace: Center the back support over your lower back (lumbar region), ensuring it is sitting comfortably.
- Fasten the Brace: Secure the front closure (typically Velcro) around your abdomen. The brace should fit snugly but not too tight to restrict breathing or movement.
- Adjust Side Pulls: Tighten or loosen the side pulls as needed to customize the level of compression and support. Make sure the brace feels secure and provides adequate support without causing discomfort.
- Wear During Activity: Use the back support during activities that may strain your lower back, such as lifting, bending, or prolonged sitting/standing. You can also wear it during exercise if advised by a healthcare provider.
- Do Not Overuse: While a back support can be helpful for pain relief and injury prevention, it’s important not to become overly reliant on the brace. Overuse can lead to weakened back muscles. Gradually work on strengthening your back through physical therapy or exercises.
Care and Maintenance
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintaining the back support. Most are hand-washable or machine-washable in a gentle cycle.
- Ensure that the brace is fully dry before wearing it again to prevent skin irritation or damage to the materials.
A back support with side pulls can be an effective tool for managing back pain, supporting posture, and preventing injury. It’s ideal for those with lower back issues who need adjustable support for varying levels of activity and comfort.
ORDER NUMBER: 501-W, 503-W, 505-W, 507-W, 507-W, 508-W, 509-W, 510-W, 511-W, 512-W
501-B, 503-B, 505-B, 507-B, 508-B, 509-B, 510-B, 511-B, 512-B
SIZE: X-Small thru 5X Large (see sizing chart to the left)
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS:
• Form-fitting 10" all-elastic with double pull side panels for additional support
• High quality Velcro™ closure for durability
• Four flexible stays in back panel for excellent support
INDICATIONS:
Ideal for providing support and compression for strains and sprains of the lower back.
SUGGESTED HCPC: L0625
Categories: Cervical, Spine & Abdominal


Table of Contents
Crutches and Canes
Crutches and canes are mobility aids used to support people with temporary or permanent physical disabilities, injuries, or impairments. Both devices help redistribute weight away from the lower limbs and assist with balance and stability during walking or standing.
Crutches
- Crutches are typically used by individuals with leg injuries, surgeries, or conditions that prevent them from putting weight on one or both legs. They are designed to support the body through the arms and upper body, allowing the legs to heal.
Types of Crutches
- Axillary (Underarm) Crutches:
- Design: These crutches are placed under the armpits and have a handgrip for the user to hold.
- Common Uses: Axillary crutches are often used for short-term injuries such as leg fractures, sprains, or post-surgery recovery.
- How They Work: The user places the crutches under their arms and presses down on the handgrips to lift and move their body forward, keeping the injured leg off the ground.
Forearm (Lofstrand)
Crutches
- Design: These crutches have a cuff that fits around the forearm and a handgrip. They are more compact and lightweight compared to axillary crutches.
- Common Uses: Often used for long-term or permanent conditions requiring extended use, such as cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, or post-polio syndrome.
- How They Work: Forearm crutches provide more freedom of movement than axillary crutches and are easier for users to maneuver in tight spaces.
Platform Crutches
- Design: These crutches have a platform on which the user rests their forearm, with the hand gripping a vertical post.
- Common Uses: Ideal for individuals who have difficulty gripping due to arthritis or other hand/wrist conditions.
- How They Work: Instead of relying on hand strength, the user places their forearm on the platform to support their weight.
Benefits of Crutches
- Weight Distribution: Crutches allow users to shift their body weight away from the legs, reducing strain on injured or recovering limbs.
- Improved Mobility: By using crutches, individuals can move around more easily, even if they are unable to bear weight on one or both legs.
- Injury Recovery: Crutches are essential for ensuring that individuals avoid putting pressure on healing bones, ligaments, or muscles.
Considerations for Crutches
- Upper Body Strength: Using crutches requires good upper body and arm strength, as the hands, arms, and shoulders bear much of the user’s weight.
- Proper Fitting: Crutches must be fitted correctly, with the top of the crutch positioned about 1-2 inches below the armpit and the handgrip at hip level.
- Risk of Nerve Compression: Improper use or prolonged reliance on axillary crutches can lead to nerve compression in the armpits, resulting in numbness or pain in the arms.
Canes
Canes are generally used by individuals who need less support than crutches. They help with balance and weight distribution and are often used by elderly individuals or those with mild mobility impairments. Canes are designed to provide support by allowing the user to lean on the cane as they walk.
Types of Canes
- Single-Point Cane:
- Design: A cane with a single tip at the bottom, typically with a curved or ergonomic handle.
- Common Uses: Ideal for individuals with mild balance issues, arthritis, or joint pain who need extra support while walking.
- How It Works: The user holds the cane in the hand opposite the affected or weaker leg, helping distribute weight and improve balance.
Quad Cane
- Design: A cane with a four-pronged base for greater stability and balance.
- Common Uses: Beneficial for individuals with more significant balance problems, muscle weakness, or neurological conditions like stroke recovery.
- How It Works: The wider base provides more stability, making it easier for individuals to maintain their balance on uneven surfaces.
Folding or Adjustable Canes:
- Design: These canes can be collapsed for easy storage and adjusted for height.
- Common Uses: Suitable for individuals who travel or need a cane only occasionally.
- How It Works: The user can adjust the cane’s height to their comfort level and fold it when not in use.
Offset Cane:
- Design: Features a handle that is positioned forward from the cane’s base, offering better weight distribution.
- Common Uses: Helpful for individuals with wrist or hand pain who need better balance and support without the strain on the hand.
- How It Works: The offset design allows for a more comfortable grip and improved stability.
Benefits of Canes:
- Balance and Stability: Canes provide a stable support point, reducing the risk of falls and helping individuals with balance issues walk more confidently.
- Weight Relief: Canes can help transfer a portion of body weight from the lower limbs to the upper body, relieving pressure on joints and muscles.
- Ease of Use: Canes are relatively easy to use and don’t require as much upper body strength as crutches.
- Portability: Canes are lightweight and easy to carry, store, and transport, making them a convenient option for people with mild to moderate mobility challenges.
Considerations for Canes
- Proper Height: It’s essential to ensure that the cane is the correct height. The handle should be at the level of the user’s wrist when standing straight with their arms relaxed.
- Gait Training: Using a cane effectively often requires instruction from a physical therapist to ensure proper gait and weight distribution.
- Support Level: Canes provide less support than crutches or walkers, so they are better suited for individuals who need minimal assistance with mobility.
Key Differences Between Crutches and Canes:
- Support Level: Crutches offer more support and are used for individuals who cannot bear weight on one or both legs, while canes are for people who need only minimal assistance.
- Upper Body Requirement: Crutches require more upper body strength and coordination, whereas canes are easier to use and require less arm strength.
- Mobility Needs: Crutches are often used for temporary, serious injuries or post-surgery recovery, while canes are typically for long-term use in cases of mild balance issues or chronic conditions.
Both crutches and canes can greatly improve mobility and independence for individuals with injuries, surgeries, or mobility impairments. They must be used correctly, with appropriate fitting and guidance from a healthcare professional, to maximize their benefits and prevent complications.