LSO BRACE _ Universal
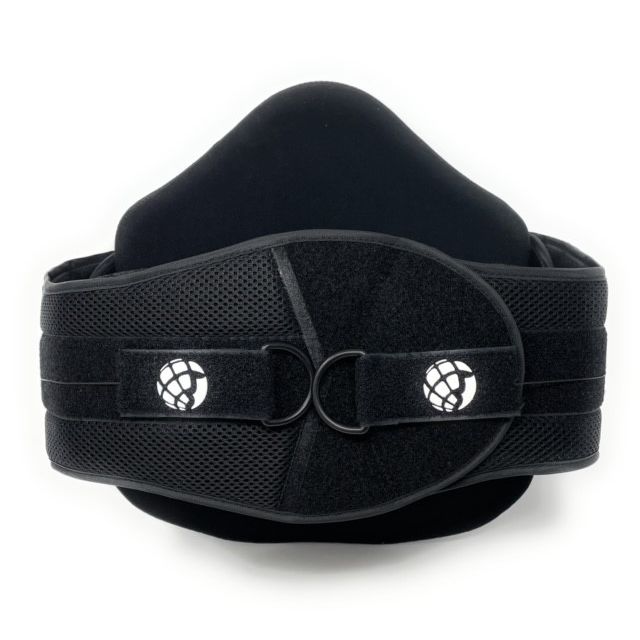
The LSO brace (Lumbosacral Orthosis brace) is an orthopedic device designed to support and stabilize the lower spine, particularly the lumbar (lower back) and sacral (pelvic) regions. It is commonly used to treat conditions like lower back pain, herniated discs, post-surgical recovery, and various spinal injuries or degenerative disorders.
SUGGESTED HCPC: 5027 - L0627 and L0642, 5031 - L0631 and L0648, 5037 - L0637 and L0650, 5039 - L0639 and L0651, 5056 - L0456 and L0457
ORDER NUMBER: 5027, 5031, 5037, 5039, 5056
SIZE: Universal (see sizing chart to the left)
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS:
• Available in 5 versions
• 5027 has a 10" back panel; the 5031 has a 14" back panel; the 5037 has a 14" back panel plus side panels; the 5039 has a 14" back panel, side panels and front panel; and the 5056 has a 14" back panel and shoulder straps
• Universal sizing system
• Adjustable pull handles to allow for optimal compression
• Breathable fabric allows air flow to keep patients cool and dry over long periods of time
INDICATIONS:
Spinal Stenosis, Spondylolisthesis, Spondylolysis, Chronic Back Pain, Spinal Instability, Post-Op Disc Surgery, Facet Syndrome, Degenerative, Hemiated, Bulging Disc, Post-Operative Lumber Fusion.
SUGGESTED HCPC: 5027 - L0627 and L0642
5031 - L0631 and L0648
5037 - L0637 and L0650
5039 - L0639 and L0651
5056 - L0456 and L0457
Categories: Cervical, Spine & Abdominal
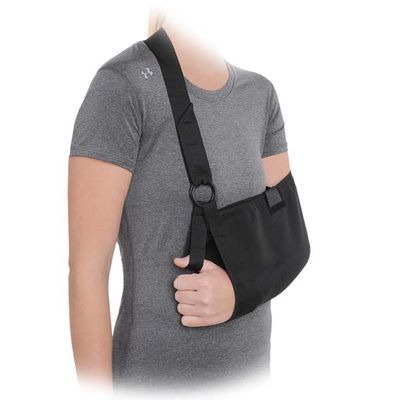
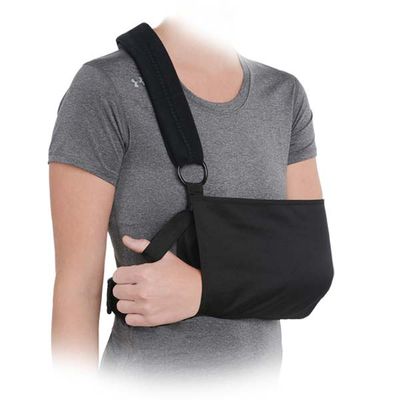
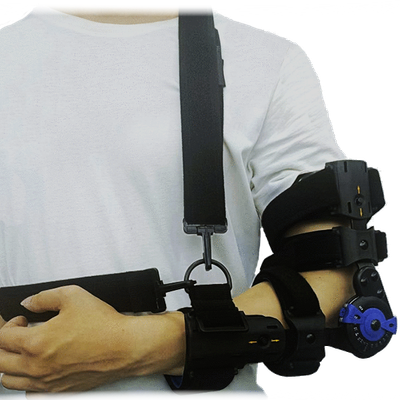
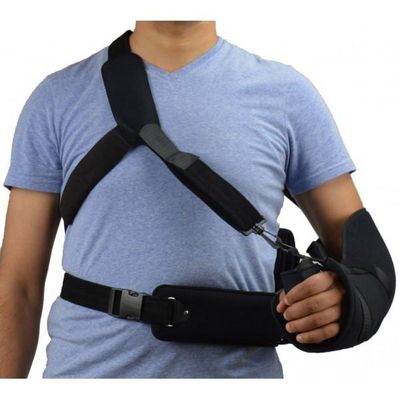



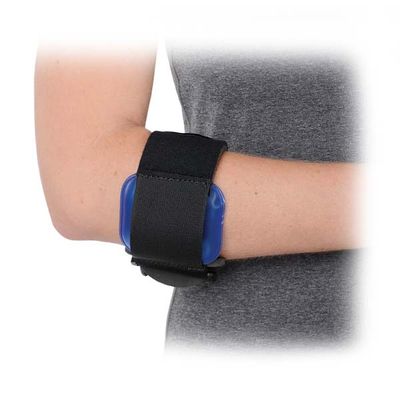
Table of Contents
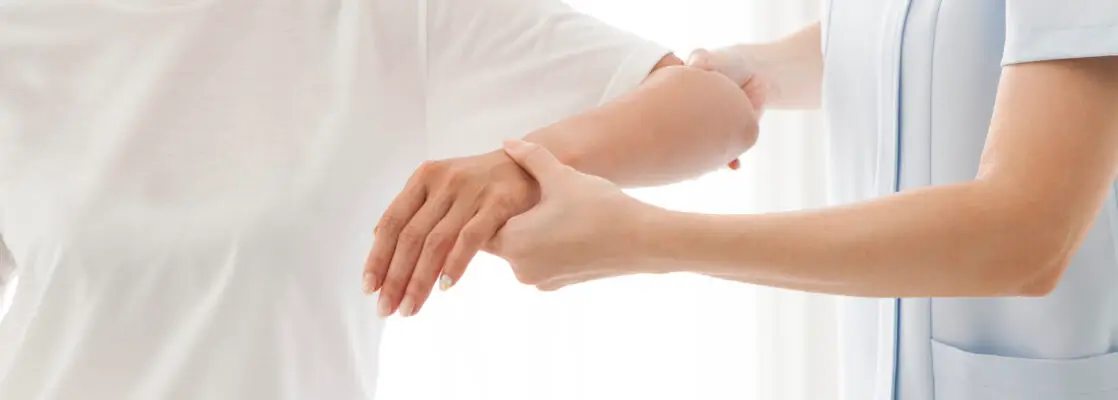
Shoulder and Elbow Brace
Shoulder and elbow braces are designed to provide stability, support, and relief from pain associated with injuries or chronic conditions affecting these joints. These braces are often used to aid recovery, improve mobility, and prevent further injury.
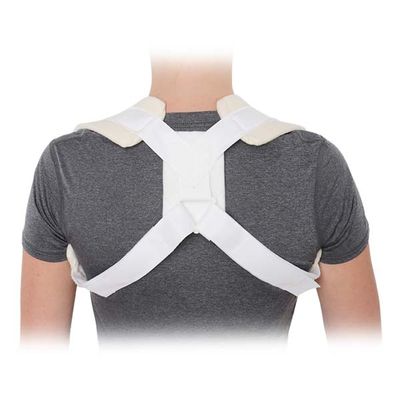
Shoulder Brace:
A shoulder brace typically provides compression and stabilization to the shoulder joint, helping to reduce pain and inflammation while promoting proper posture. Shoulder braces are often used for:
- Rotator cuff injuries: To protect and support the shoulder after a tear or strain.
- Shoulder dislocations: To stabilize the joint and prevent further dislocations.
- Post-surgical recovery: Assisting with immobilization and gradual rehabilitation.
- Chronic instability: Preventing overuse injuries and reducing the risk of reinjury during physical activity.
Features of a Shoulder Brace:
- Compression: Helps to reduce swelling and pain.
- Adjustable Straps: Allow for customized support and positioning.
- Breathable Materials: Keep the shoulder area cool while providing support.
- Immobilization: Some shoulder braces restrict movement for more severe injuries, while others allow for controlled range of motion.
Elbow Brace:
An elbow brace is commonly used to support the elbow joint, reduce strain, and alleviate pain. They are often used for conditions such as:
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis): A common overuse injury where the brace applies pressure to the forearm muscles, reducing strain on the elbow tendon.
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): Similar to tennis elbow, but affects the inner side of the elbow.
- Elbow sprains and strains: Supporting the joint during recovery to prevent further damage.
- Post-surgery: Stabilizing the elbow after surgical procedures to promote healing.
Features of an Elbow Brace:
- Targeted Compression: Helps to relieve pain and inflammation in specific areas.
- Adjustability: Allows users to control the level of compression and support.
- Lightweight and Breathable: Ensures comfort during prolonged use.
- Range of Motion Control: Some braces have hinges to control how much the elbow can bend.
Both shoulder and elbow braces are important tools for athletes, manual laborers, or individuals recovering from injuries or surgery. They can be used for rehabilitation, pain management, and injury prevention.
Shoulder and Elbow Pain
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain:
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: This is one of the most common sources of shoulder pain. It occurs due to strain or tears in the muscles and tendons around the shoulder joint.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): This is characterized by stiffness and reduced mobility in the shoulder joint.
- Tendinitis or Bursitis: Inflammation of the tendons or bursae can cause sharp, localized pain in the shoulder.
- Arthritis: Wear and tear in the shoulder joint can lead to osteoarthritis, causing chronic pain and stiffness.
- Dislocation: When the upper arm bone is forced out of the shoulder socket, it can cause intense pain and instability.
Common Causes of Elbow Pain:
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis): This occurs due to overuse of the forearm muscles, leading to pain on the outside of the elbow.
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): This condition causes pain on the inside of the elbow, often due to repetitive stress.
- Olecranon Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa at the tip of the elbow can cause swelling and pain.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the ulnar nerve near the elbow can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the forearm and hand.
- Elbow Arthritis: Like the shoulder, the elbow can suffer from arthritis, leading to joint stiffness and discomfort.
Treatment and Management:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing activities that aggravate the pain can help prevent further damage.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises for the shoulder and elbow muscles can relieve pain and restore function.
- Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or ice packs can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Bracing: Supportive braces, such as a tennis elbow brace or a shoulder sling, can help offload the affected joints and promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, such as rotator cuff tears or advanced arthritis, surgery may be necessary.
If shoulder or elbow pain persists, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.